This is tutorial 2 for Arduino. Readers will learn on how to program LED blinking using Digital Pin of Arduino UNO. In this tutorial, Pin 12 of digital I/O will be used as an output. There are already built-in LED Pin 13 in this board. But in this tutorial we will use external LED and connects with digital Pin of Arduino UNO.
1. Prepare all the components:
Before we start with the tutorial, you need to prepare all the require components. You will need Arduino Uno board, breadboard, 1K Ohm resistor, LED, USB cable and laptop. Below is all the items required in this tutorial. |
| Arduino Uno Board |
 |
| Breadboard |
 |
| 1k ohm Resistor |
 |
| LED |
 |
| USB cable |
 |
| Laptop |
2. Draw a schematics:
Now will all components prepared, we will draw a schematic so that we will refer to this connection before we connect them. |
| LED Blinking Tutorial Schematic |
3. Connects all components:
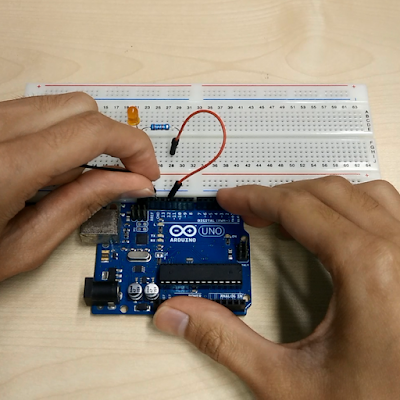
We will connect GND Pin and Pin 12 of Arduino to breadboard. GND pin will be connect to negative pin of LED while Pin 12 will connect with resistor. Resistor will connect with positive Pin of LED. |
| Connecting all components for LED blinking tutorial. |
4. Program Arduino with LED blinking interval of 1 second:
Now, let's write the first code. The first code is to make LED blink with 1 second interval. Arduino will send HIGH signal to Pin 12 with 1000 ms delay and then LOW signal to Pin 12 with 1000 ms. This code will continuously run as they are in the Void loop. |
| Arduino code for LED blinkin with 1s interval |
 |
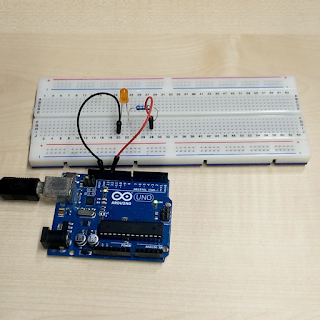
| LED blinking demo with 1s interval (Turn ON) |
 | |
|
5. Program Arduino with LED blinking interval of 0.2 second (faster):
Now, let's write the second code. We will modified previous code to make it blinks faster. Delay value of 1000 is changed to 200.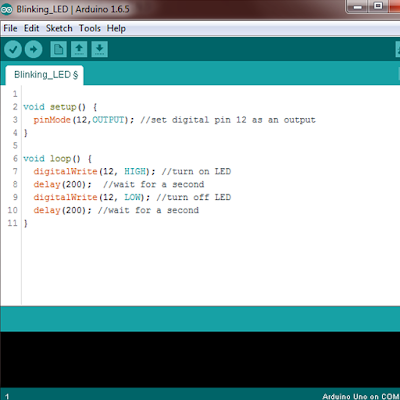 | |
|
 |
| LED blinking demo with 0.2s interval (Turn ON) |
 |
| LED blinking demo with 0.2s interval (Turn OFF) |
DONE!
Below is video tutorial for this LED blinking.
Arduino LED blinking or blink led tutorial projects Part 2
Steps:
1. Prepare all components
2. Draw a schematic
3. Connect all components
4. Program Arduino with LED blinking interval of 1 second
5. Program Arduino with LED blinking interval of 0.2 second
1. Prepare all components
2. Draw a schematic
3. Connect all components
4. Program Arduino with LED blinking interval of 1 second
5. Program Arduino with LED blinking interval of 0.2 second